

The motion of individual atoms, ions, or molecules in a solid is restricted to vibrational motion about a fixed point. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass), and are typically low in energy. Solids are similar to liquids in that both are condensed states, with particles that are far closer together than those of a gas.
The first theory explaining mechanism of melting in the bulk was proposed by Lindemann, who used vibration of atoms in the crystal to explain the melting transition. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure. Below the melting point, the solid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the liquid form is preferred.
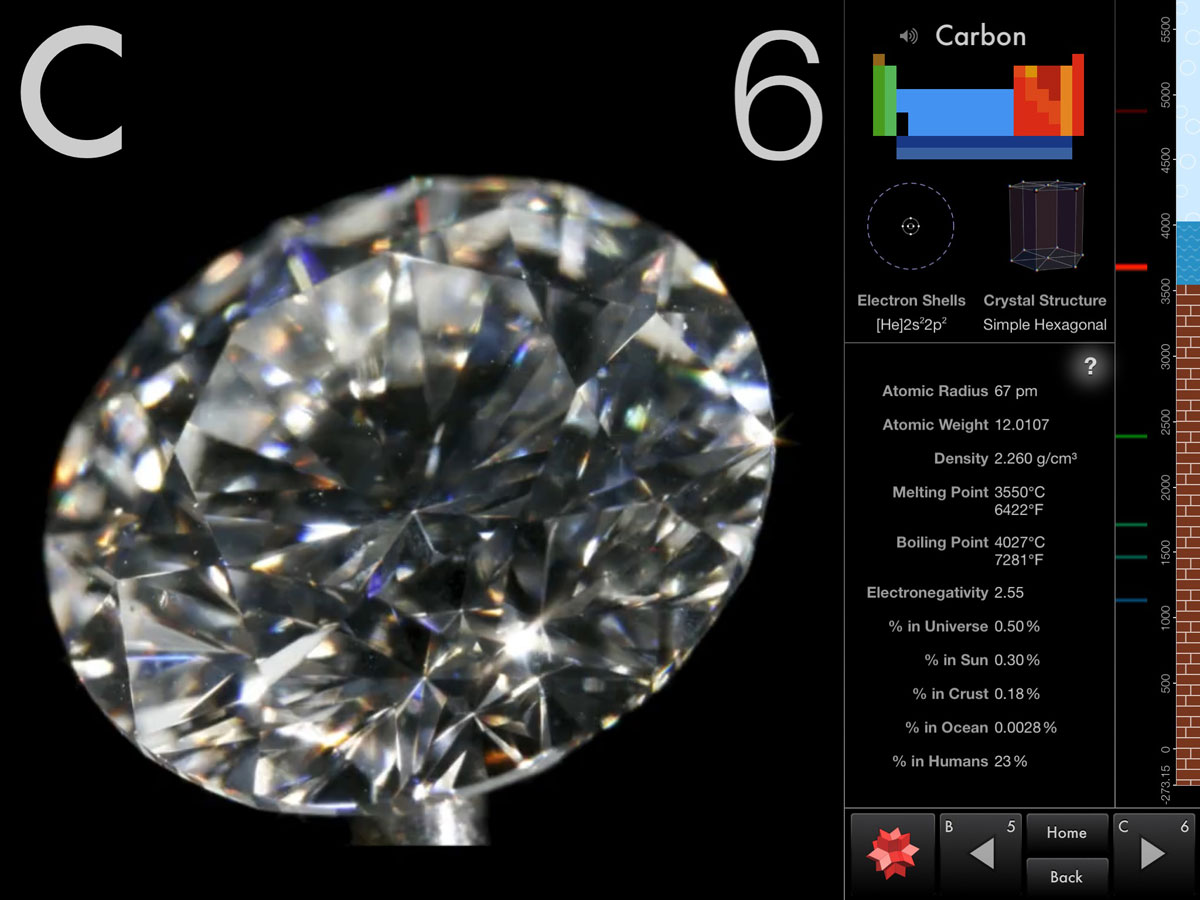
Carbon element free#
At the melting point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Adding a heat will convert the solid into a liquid with no temperature change. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
